常见检测点
检测 gmain 和 gum-js-loop
frida 在注入时, 会在目标进程下创建两个新线程,名为 gmain 和 gum-js-loop.
通过检测线程名,可以判断当前进程是否被frida注入. 具体实现方法 可以通过判断 /proc/self/task/tid/status 文件, status文件的第一行是线程名.
遍历所有的线程名, 如果发现 gmain 和 gum-js-loop, 则可认定该进程被注入.
下面给出检测代码
检测 gmain 和 gum-js-loop
1 | static const char *APPNAME = "DetectFrida"; |
检测 frida 特征命名管道 “linjector”
1 |
|
对比内存中的可执行段(.text 段等)与磁盘上的 ELF 文件内容,识别是否被 Frida 等工具篡改注入
1 | //Structure to hold the details of executable section of library |
来看看一些绕过 frida检测的项目 strong-frida
这里只patch 了针对 gmain 和 loop-js 还有命名管道的检测.
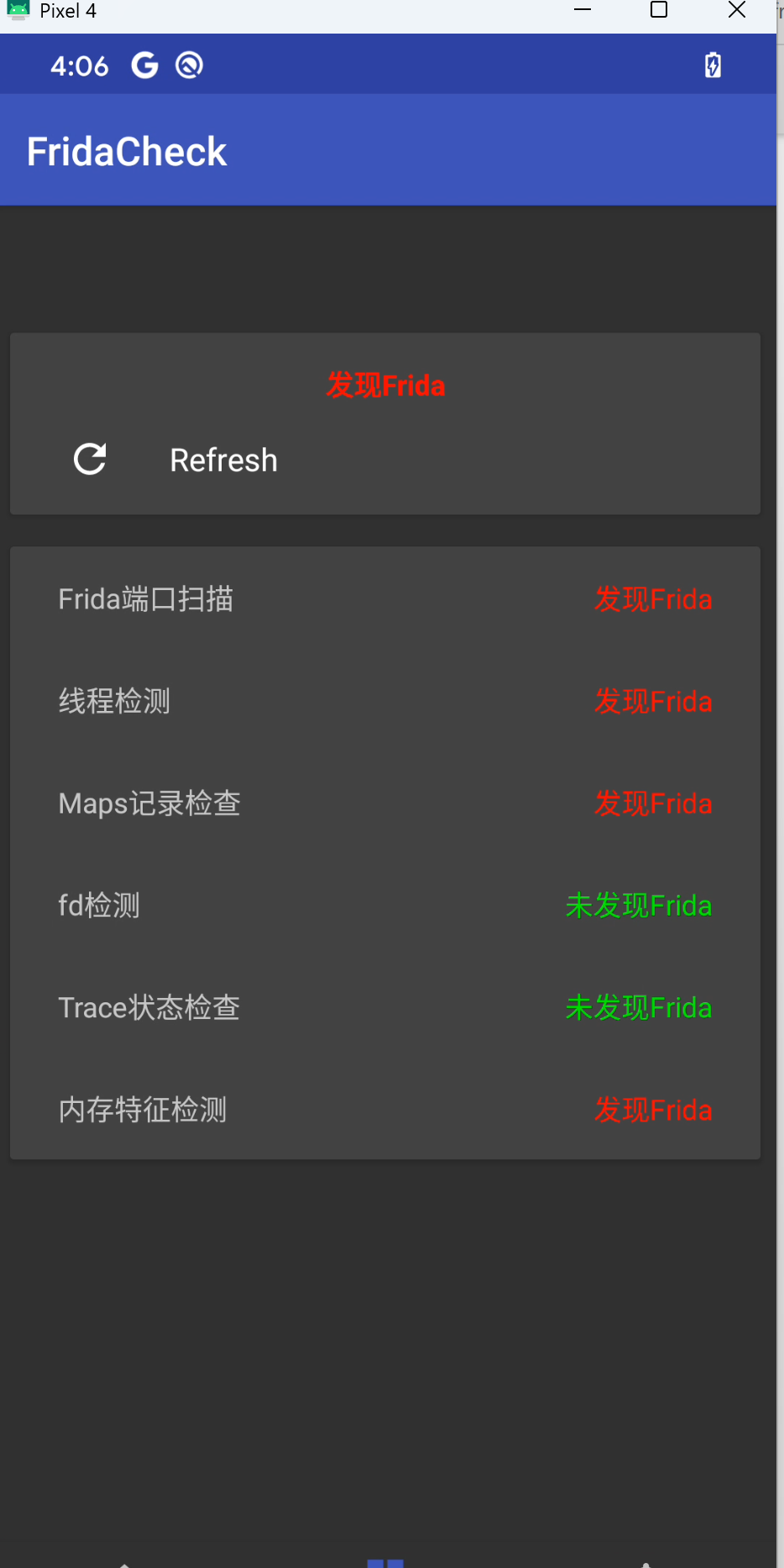
这里放一个 frida check 的apk, 可自行验证
这里延申一种定位加密位置的办法, 很好用
试试看 hook StringBuilder StringBuffer 的 toString , 然后打印调用堆栈.
1 | Java.perform(function x() { |
样例分析
如果一个样本存在 anti-frida, 要怎么定位关键监测点呢
先试试看 hook 库的加载函数(在 Android 较低版本比如 6.0 上是dlopen,较高版本上是android_dlopen_ext)
1 | var android_dlopen_ext = Module.findExportByName(null, "android_dlopen_ext"); |
每次加载完一个so文件后, 就休眠一段时间, 如果程序退出了, 那么凶手可能就是最后一个加载的so文件.
针对 libmsaoaidsec.so 的分析, 可以看看之前发过的文章, 使用 stackplz 分析 libmsaoaidsec.so, 很方便.
其实也可以简单绕过
1 | function hookDlopen() { |
或者 明明要加载 libmsaoaidsec.so,让程序再加载一个空 或者加载一个已经加载过的so文件.
1 | function hook_dlopen(soName = '') { |